E-mail trigger
The email trigger, starts a transfer after receiving an email. Emails in MIME format are also processed.
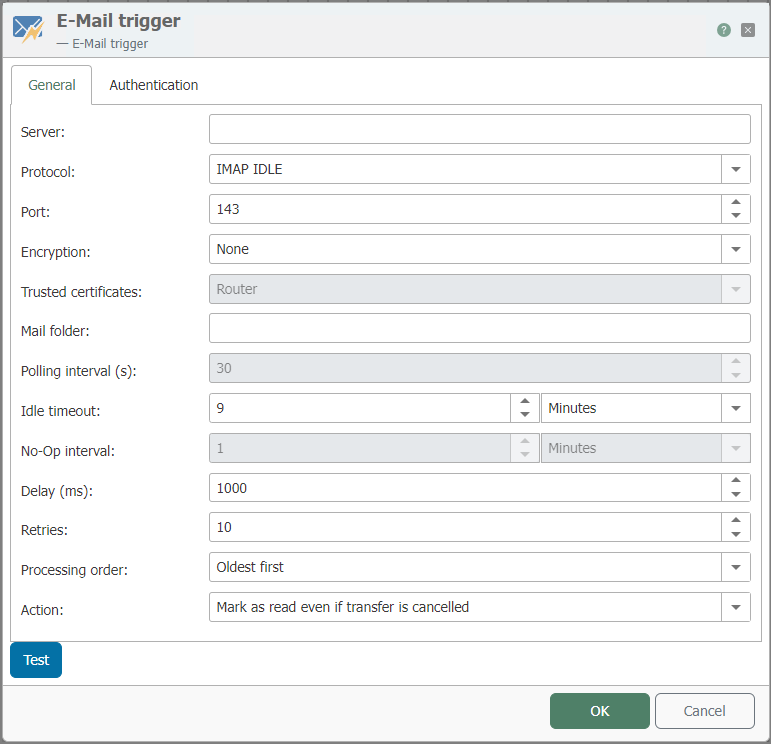
The followind properties can be configured:
| Server | The address of the email server |
| Protocol | Select your preferred protocol |
| Port | Enter the TCP port of the mailserver |
| Encryption | Select:
|
| Trusted certificates | Set which certificates should be trusted:
|
| Mail folder | A "Mail folder" in an email trigger is a specific location within an email application where the trigger is set to monitor for new email. When setting up an automated workflow, such as with Microsoft Power Automate, you can specify which mail folder (such as Inbox, Sent Items, or a custom folder) the trigger should monitor. When a new email arrives in the specified folder, the trigger can initiate a predefined action or workflow. |
| Polling interval (s) | Select the interval to check for new mails |
| Idle timeout | The connection is kept open by the router for a set period of time. If no emails are received, the time restarts. If an email is received during this period, the timeout is terminated immediately. Attention: This function must be supported by the email server. |
| No-Op interval | Refers to a time period during which the trigger checks for new emails but takes no operation (no-op) if no new emails are found. |
| Delay (ms) | Refers to the amount of time, in milliseconds, that the system waits before executing the next action after the trigger conditions are met. This setting is useful for ensuring that actions do not overlap or execute too quickly, which can be important when dealing with email processing where timing is crucial. |
| Retries | Count of retries before a transfer gets cancelled |
| Processing order | Select which emails are processed first |
| Action | Select whats happening to the emails after the transfer |
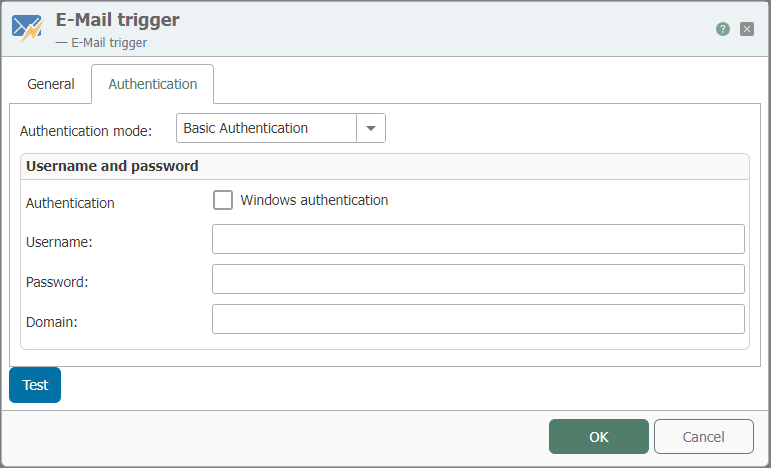
| Authentication mode | Refers to the method by which the email system authenticates a user or service before allowing access to trigger an email-based workflow. This setting is crucial for security and ensures that only authorized entities can initiate the email trigger. |
| Windows authentication | Uses alternatively the user, under which the router service runs (Standard: “System”). |
| Username | This is the username of the account that is being used to authenticate. |
| Password | The secret key associated with the user account. |
| Domain | This property is relevant when using Windows Authentication. The domain refers to the group of computers, users, and devices that are managed together and operate under the same set of rules in a network. Providing the domain name is essential for authentication when the user account is part of a Windows domain network. |