Database Transfer Object
Databases are available both as source and destination of data transfers. The database set of access data has to be specified within plug-in configuration. Create a DB transfer object as described above.
Database Transfer Object
Configure the object’s properties by double click:
| DB access data | Select one of the configured sets of access data |
| Type | Select: Queries one or more rows from a table or a view. You have to define filter and sorting criteria as well. Thus, the transfer object will work as datasource. Insert: Inserts a new row into a table. Thus, the transfer object will work as destination. For a database insert, incomplete arrays are padded. For example: If a single entry from a timestamp and several entries from an array should be read into a database, so the time stamp for the individual variables of the array can be done. The timestamp is therefore automatically used multiple times, until all variables have been read. Therefore, applies: An insert always determines the highest InsertCount. Entrys with smaller count are then expanded by a factor of X, so that the values in the table are filled up. Also selectable for views. Update: Updates one or several rows within a table. You have to define filter criteria as well. Thus, the transfer object will work as destination. Also selectable for views. Delete: Deletes one or several rows within a table. You have to define filter criteria as well. Also selectable for views. Stored procedure: Executes a stored procedure as soon as trigger conditions are met. Define parameter values (as destination) and use return values as source. |
Important: If the type is set to “Stored Procedure”, OPC Router will execute this Procedure immediately, submitting default parameters (string = NULL, int = 0 etc.). Thus, OPC Router detects the structure of the result set. Procedure will be rolled back. This means, that the Stored Procedure called must be transaction safe and must not return errors on default parameters.
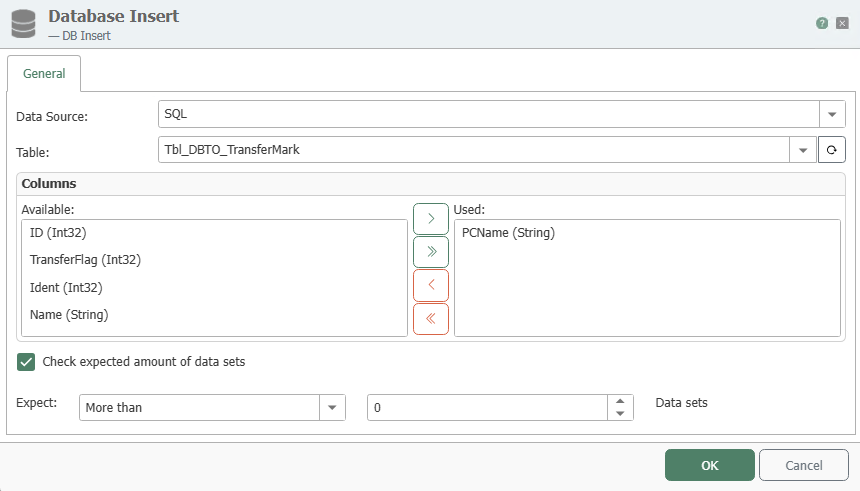
Tab General (all types)
| Table (View, Stored Procedure) | Table, View or Stored Procedure this object refers to. Note: Table has to have a primary key. Tables without primary key are not supported. |
| Available columns/Columns used | (View/Table operations) Available columns: Columns available in table or view, but not assigned to this object yet. Columns used: Columns assigned to this object and thus shown as items within this objects (to be used as source or destination). This distinction is made to keep the layout well-arranged, e. g. imagine you only need one out of 30 columns. So only this one column is shown in the connection layout. Move columns by double click onto their names or by the buttons provided (after having selected the columns). Buttons “Up” and “Down” will sort the columns (again, this is to keep the layout well-arranged) Stored Procedure: The lists show input and return parameters. |
Tab Filter (Select, Update, Delete)
| Filter | Shows filters and filter groups. From this tree, the SQL statement is constructed. Filter values can be inserted dynamically during runtime. Use Variables/Constant values to insert constant filter criteria. Use Add-buttons to add filters or groups. Delete will remove the selected entry. Filter types: EQUAL: Compares if values are equal. GREATER: Compares if value is greater. GREATER_OR_EQUAL: Compares if value is greater or equal. SMALER: Compares if value is smaller. SMALER_OR_EQUAL: Compares if value is smaller or equal. NOT_EQUAL: Compares if values are not equal. LIKE: Compares strings. LIKE_WILDCARD: Equal to LIKE %WERT%. LIKE_WILDCARD_END: Equal to LIKE WERT%. IN: Compares multiple values. Value input is an array. NOT_LIKE: Compares if strings are not equal. NOT_LIKE_WILDCARD: Equal to LIKE_WILDCARD but negated. NOT_IN: Compares if multiple values are not equal. Value input is an array. |
| Edit filter/filter group | Entries are shown dependent on selected entry. Junction: Defines whether filters are linked with AND or OR. Column: Column to be filtered Relational operator to compare values |
| Preview | Preview of SQL Statement, e. g. WHERE (UtcTimeStamp >_ ?) AND (Value = ?) . Here, all rows would be selected with a TimeStamp newer than the filter and with a value equal to the filter. The values of the filter criteria have to be inserted during runtime. Thus, you can provide e. g. values of OPC items or other tables as criteria. If the filter should be static, simply project a constant value object and transfer its value into the filter. |
After confirming with “OK”, you will see filter criteria as elements (items) of this transfer objects. Draw connection arrows from any source to assign values during runtime. With time filters, relative filter criteria like “-1d” (=yesterday) are allowed.
Tab Query (Select)
| Sorting order | Ascending/Descending |
| Sorting by column | Column with sorting criteria. |
| Do not change records | Transferred records will not be changed. |
| Mark records after successful transfer | (only with select from table) In the column specified below, for every row transferred successfully, a “1” is inserted, a “2” if an error occurred. Note: In the table concerned, a simple primary key to the numerical column "ID" is required. |
| Column to mark | (only with select from table) Column to mark transferred rows. Default value set by database should be “0” |
| Count failed transfers | count the failed transfers Note: Select at “Error column” the column in which the number of failed transfers is to be counted up. |
| Delete records after successful transfer | only with select from table) Transferred rows will be deleted. CAUTION: Rows in database table will be deleted without recover possibility. |
| Abort transfer (with empty result) | If the result set is empty, the transfer is canceled. |
| Return read error (with empty result) | If the result set is empty, the transfer is canceled and an error is logged in log file and status monitor. |
| Return empty record | Returns an empty record for an empty query result. |
| Limit number of records | Transfers only the specified number of rows/records. Be sure to have you result set sorted correctly. |
Example: If only the newest record is to be transferred, then sorting column should be e. g. a “UtcTimeStamp” with Sorting order “Descending”, the number of records limited to “1”.
Note: If the type is set to “Update”, the transfer object will provide the number of rows updated as source.
Check expected amount of data sets
Activate this option to check the correct size of the data to be used for the insert. If you receive an array of data, for example, you can define here the minimum, maximum or exact number of data sets the array must have for the insert to be carried out.
Select always with filter
Use SQLSelect only with filters (WHERE clause) so as not to load the whole table into memory. In conjunction with transfer marks, you filter, for example, after <Transferflg> <> 1
Mark transferred records
Mark transferred records. In your tables, keep columns in which the OPC Router can mark transferred data records (“Transfer flag” not transferred, transferred, transfer error). The transfer flag columns should be set to the default value of “0” and should not be allowed to assume NULL, so that a correct assignment to the three status are always guaranteed.
Index transfer flag
To improve performance, the transfer flag column should be indexed as follows:
-
If the OPC Router should filter by
transfer flag = 0:CREATE NONCLUSTERED INDEX [IX_TransferTable_Transferflag] ON [dbo].[TransferTable]
(
[Transferflag] ASC
)
WHERE ([Transferflag]=(0))
GO -
If the OPC Router should filter by
transfer flag <>1:CREATE NONCLUSTERED INDEX [IX_TransferTable_Transferflag] ON [dbo].[TransferTable]
(
[Transferflag] ASC
)
WHERE ([Transferflag]<>(1))
GO
Sort select results
Sort the table in ascending order after the transfer flag. This way, the untransferred records are transferred first; erroneous individual transfers are only attempted again at the end of the transfer. For performance optimization, filtering can be done after the transfer flag column (transfer flag = 0 or = 2). A correspondingly filtered index can be created in the database for this purpose.