MQTT Cloud Profile: Azure IoT Hub
This chapter describes the additional “Azure” tab of the MQTT plug-in. All general MQTT settings (default profile) can be found under MQTT Plug-in Configuration.
Principle: The Azure tab supplements the standard configuration with fields for authentication via shared access keys (SAS tokens) and device IDs for secure access to the Azure IoT Hub.
Tab: Azure
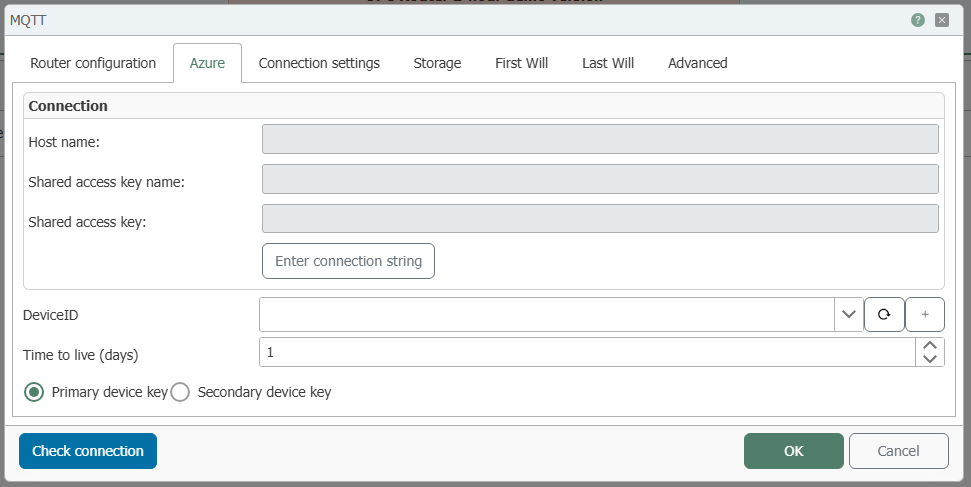
Recommended introduction according to step-by-step instructions: Enter connection string, Select/create device, Check connection. For details, see [Knowledge Base article].
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Host name | Host name of the Azure IoT Hub. Displayed in Azure in the IoT Hub → Overview → Hostname area (e.g., myhub.azure-devices.net). |
| Shared access key name | Name of the policy (e.g., iothubowner or user-defined policy) from the Azure IoT Hub. |
| Shared access key | The corresponding key for the selected policy. Displayed in Azure under Shared access policies. |
| Enter connection string | Opens a pop-up window for direct entry of the complete connection string (HostName=...;SharedAccessKeyName=...;SharedAccessKey=...). |
| Device ID | Unique device ID in the IoT Hub. Displayed or newly created in the Azure portal under IoT devices. |
| Time to live (days) | Lifetime of the generated token in days. After expiration, a new token is automatically created from the access key. |
| Primary / Secondary device key | Select whether the primary or secondary token is used for authentication. |
| Check connection | Tests the connection to the specified IoT Hub and token. |
Prerequisites in Azure IoT Hub
- Create IoT Hub: Via Azure Portal → Create a resource → Internet of Things → IoT Hub.
- Create device: IoT Hub → Devices → + New → Define device ID → Save.
- Check access policy: Under Shared access policies, ensure that a policy with write permissions (
iothubowneror your own policy) is available. - Copy access data:
-
Hostname (e.g.,
example.azure-devices.net) -
Shared Access Key Name (policy)
- Shared Access Key (token)
Certificates / Security
- Azure IoT uses TLS by default for all MQTT connections (port 8883).
- Therefore, TLS/SSL must be enabled in the Connection settings.
- Manual certificate selection is usually not necessary, as Azure secures the connection using public root certificates.
Configuration in the MQTT plug-in (Azure tab)
-
Open Plug-ins → MQTT and create/edit a connection.
-
Router settings: Select the Azure IoT cloud profile.
-
Azure tab (recommended according to the tutorial):
-
Click Enter connection string and insert the Primary connection string of the desired policy (e.g.,
iothubowner). -
Select DeviceID or create a new one using +. 3. Run Check connection.
-
Alternative: Enter hostname / shared access key name / key manually (instead of connection string).
-
Check Connection settings / First Will / Last Will / Advanced if necessary; then save with OK.
Typical settings / notes
- QoS: See MQTT Performance for details on latency and throughput.
- Storage: For persistent “Last Value” queries, enable MQTT Data Storage (see MQTT Storage Read Transfer Object).
- Client ID: Should correspond to the device ID if multiple devices are connected to the same IoT Hub in parallel.
- TLS port: Default is 8883, alternatively WebSocket via port 443 (not recommended for OPC Router).
Troubleshooting
| Symptom | Cause / Solution |
|---|---|
| 401 Unauthorized | Incorrect or expired SAS token. Check time to live and regenerate token if necessary. |
| Device not found | Device ID does not match Azure IoT Hub. Check in the device list. |
| Connection refused (Port 8883) | TLS disabled or port blocked. Check firewall and TLS settings. |
| Access denied (Policy) | Missing policy permission. Enable read/write access in Azure Policy. |
See also
- Main configuration: MQTT Plug-in Configuration
- Performance / QoS / RTT: MQTT Performance
- Storage Read: MQTT Storage Read Transfer Object